It is often quite difficult to identify a deficiency or toxicity symptom in the field because they never really occur as a single element deficiency or toxicity. Each of the elements are inter dependent and they influence each other within certain ratio’s. One would find for instance that phosphorus toxicity, is expressed as either a [...]
Cotton Aphid, or Aphis gossypii, is one of the more common insect pests found in almost all vegetable crops and gardens. They vary significantly in body size and color (from bright yellow, green and dirty brown olive), and adults may have transparent wings or wingless. Damage cause by Cotton Aphids Cotton aphid infestations may result [...]
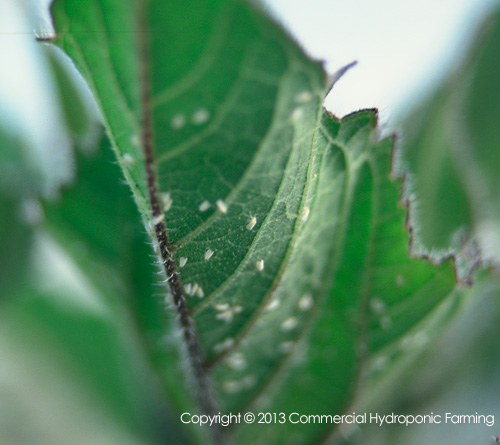
Description Greenhouse white fly, also known as Trialeurodes vaporariorum is a sap feeder. The easiest way to find white flies is to brush or shake the leaves and look for the white fly adults which fly off. Inspect the undersides of the leaves for the flies. These pets are important vectors of diseases which are [...]
Diseases of crops grown and closed hydroponic systems can be a problem and occasionally catastrophic. However, the presence of a pathogen does not necessarily mean that a disease outbreak will occur. Although not fully understood, there are fine balances in hydroponic systems involving climate conditions, biological control agents, etc. that can keep pathogens in check. [...]
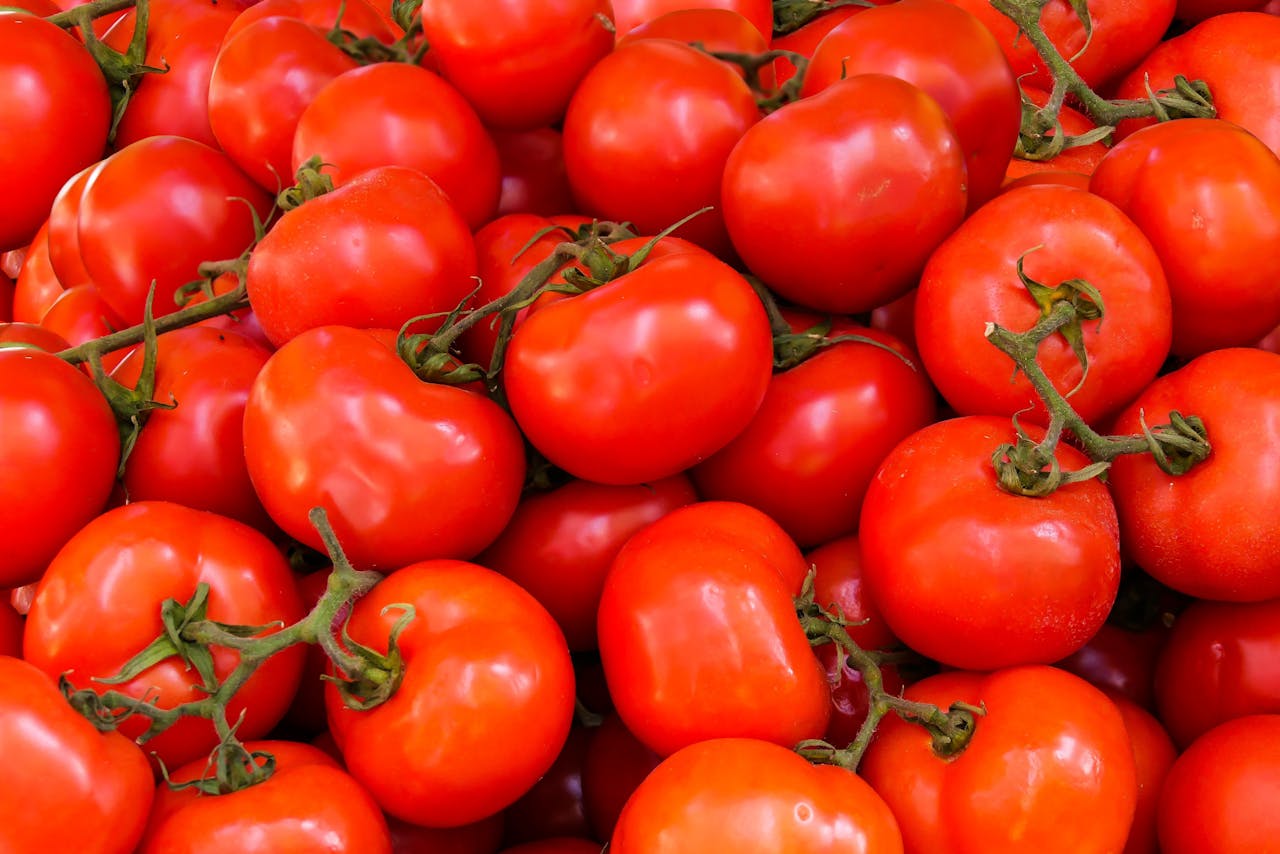
Tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum) is the world's most valuable fruit and essential greenhouse crop. They deliver vital nutrients to our diets and serve as a pivotal model for plant biology research. Unfortunately, modern tomato varieties often lack the flavour that original or traditional cultivars boast. During the domestication and enhancement process, breeders prioritized traits like yield, [...]
Factors determining plant temperature in a greenhouse. Radiation or heat energy can be reflected, transmitted, absorbed, conducted, re-radiated or used to evaporate water. Evaporation requires more than 500 calories per gram of water evaporated. It is evident that if radiant energy is absorbed, plant temperature must increase until an equilibrium is reached at higher values. [...]
There are various ways viruses can spread throughout the greenhouse. Transmission or method of spreading depends on the virus genes. A virus cannot move from one plant to another by themselves. They must be transmitted by a vector or another organism, most of the time they are insects. Each virus will have a very specific [...]
The intricate relationship between the fruit's acidity and sugar content affects how it tastes. A modest role is also played by other substances such as tannins, water-soluble minerals, and volatile chemical molecules. Two of the key elements that affect how fruit tastes are its acidity and sugar level. Fruits with a high acidity level typically [...]
Everyone has become more knowledgeable about the spread of viruses and the diseases they cause. Just like the COVID virus, we have to understand the life cycle of each virus that cause diseases in greenhouse crops. Effective virus disease control requires controlling or shutting down three important links; the source of the virus, the vector [...]
The nutrient content of water soluble hydroponic fertilizers is not always clearly indicated on packaging. It is fine that fertilizer companies take control out of our hands by formulating nutrient solutions for us, but there are times that we want to take control ourselves. That usually happens when things are not working out and yields [...]