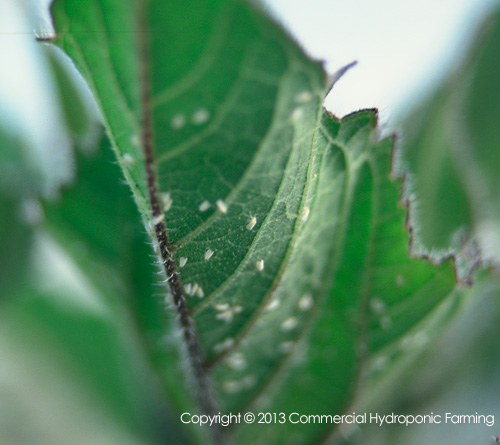
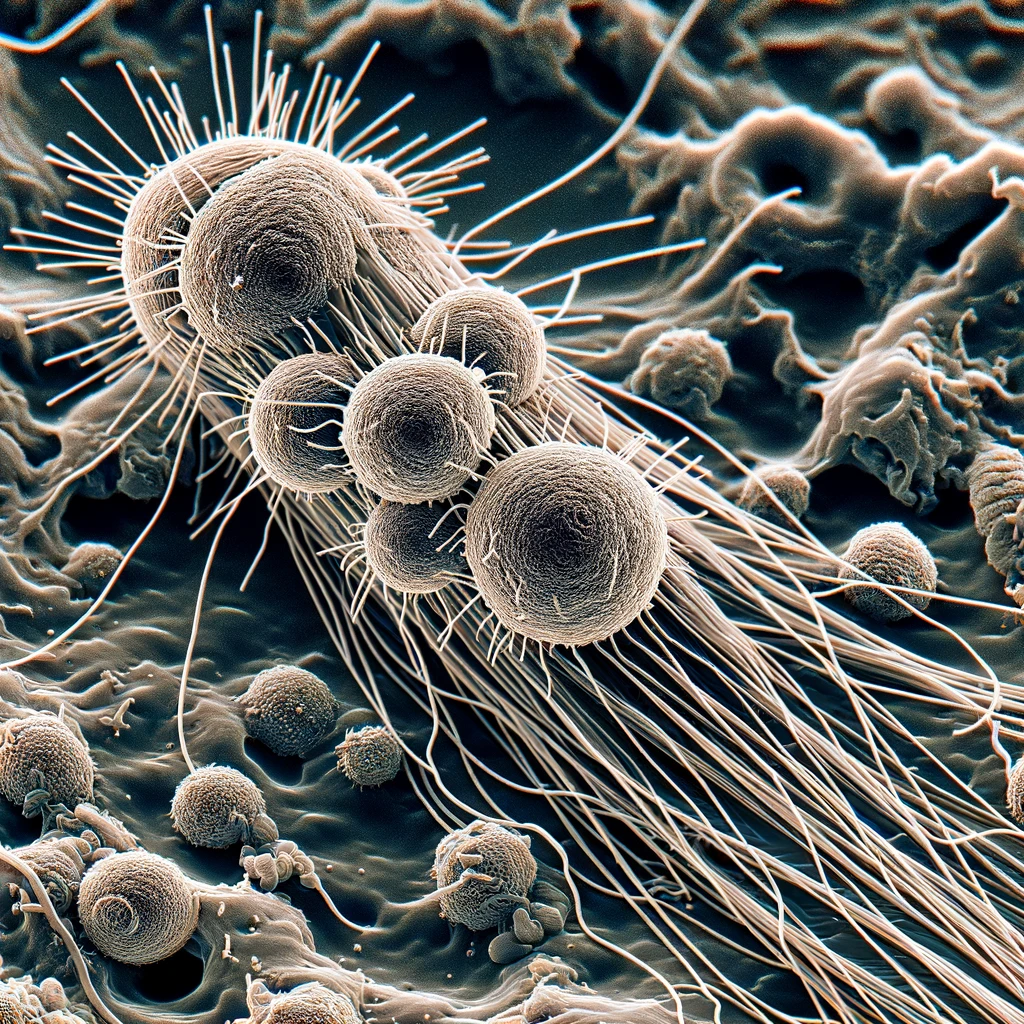
Cotton Aphid, or Aphis gossypii, is one of the more common insect pests found in almost all vegetable crops and gardens. They vary significantly in body size and color (from bright yellow, green and dirty brown olive), and adults may have transparent wings or wingless. Damage cause by Cotton Aphids Cotton aphid infestations may result [...]
Description Greenhouse white fly, also known as Trialeurodes vaporariorum is a sap feeder. The easiest way to find white flies is to brush or shake the leaves and look for the white fly adults which fly off. Inspect the undersides of the leaves for the flies. These pets are important vectors of diseases which are [...]
Diseases of crops grown and closed hydroponic systems can be a problem and occasionally catastrophic. However, the presence of a pathogen does not necessarily mean that a disease outbreak will occur. Although not fully understood, there are fine balances in hydroponic systems involving climate conditions, biological control agents, etc. that can keep pathogens in check. [...]
There are various ways viruses can spread throughout the greenhouse. Transmission or method of spreading depends on the virus genes. A virus cannot move from one plant to another by themselves. They must be transmitted by a vector or another organism, most of the time they are insects. Each virus will have a very specific [...]
Everyone has become more knowledgeable about the spread of viruses and the diseases they cause. Just like the COVID virus, we have to understand the life cycle of each virus that cause diseases in greenhouse crops. Effective virus disease control requires controlling or shutting down three important links; the source of the virus, the vector [...]
Well planned spray programs are more effective than unplanned, random chemical applications. Have you ever considered spraying when there is no pests or diseases? Poorly planned spray programs or not following a spray program has the same effect. It costs a lot of money with no advantage other than the chemical supplier. Even nature loses, [...]
The disease is found in conditions if high humidity, especially in poor ventilated greenhouses or where the ventilation is not controlled properly. Optimum temperature for disease development is between 24-27°C (75.2 - 80.6°F)Bradbury, J.F. 1967. Pseudomonas lachrymans. Description of Pathogenic Fungi and Bacteria, No 124. Commonwealth Mycological Institute, Kew, England. It is caused by Pseudomonas syringae pv. lachrymans [...]
Resistance to chemicals is due to the intense selection pressure exerted on the population that is controlled. There is only a limited number of chemicals that are effective to control pests and diseases. This causes a high intensity selection pressure with limited products with the result that evolution is set in overdrive mode. Traits resistant [...]
Tipburn in lettuce has been a problem since the first farmer planted lettuce. Any grower will at some stage have the problem occur to some extent on his farm during warmer periods. The classic tipburn symptom is necrosis of the tips of rapidly growing young leaves. Tipburn is visible externally on butterhead and cos types, [...]