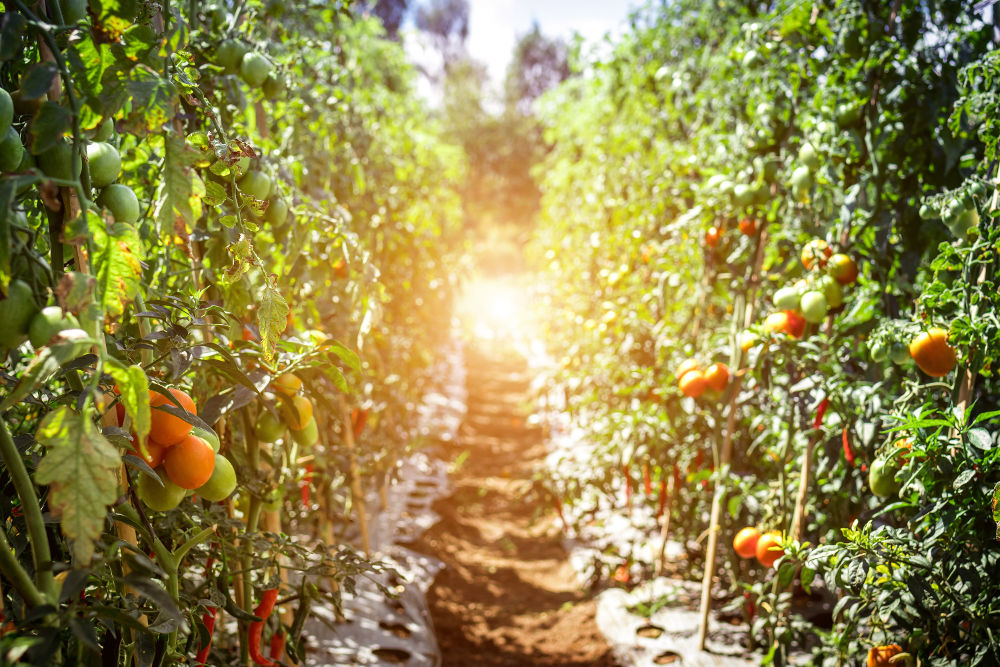
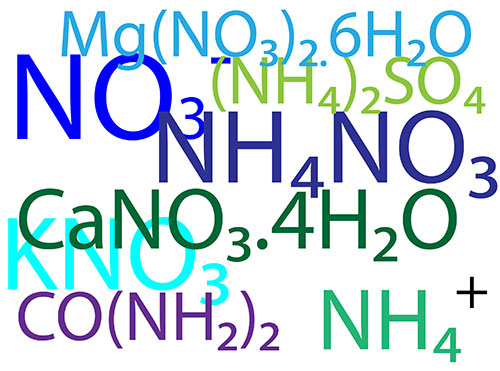Micro-elements are quite often referred to as the “trace” elements since they are used in such minute quantities in the nutrient solution. Micro-elements tend to be catalysts rather than fixed in any structure. They tend to be mobile in the plant and the difference between toxic levels and deficient levels is quite narrow. Although micro-elements [...]
Sulphur (or sulfur)is also known as the “ignored primary nutrient” since not many people realize that it is one of the macro nutrients and is extremely important. The role of S has been ignored for long times since its effect on plant growth was not known. Researchers inadvertently applied large amounts sulphur through the use [...]
Magnesium was discovered by Nehemiah Grew in 1695 by evaporating mineral waters in Epsom England. It was only in 1808 that Sir Humphrey Davy isolated the metal and identified it as magnesia oxide and termed it magnium. The metallic magnesium was first isolated by A. Bussy in 1828 and in 1883 the first metallic magnesium [...]
On average, more growers have calcium (Ca) related problems than any other nutrient. These problems occur in areas of low humidity and high temperatures. Calcium forms part of cell walls and any deficiency is marked by the breakdown of cell tissue leading to some form of internal “browning”. The average concentration in the plant varies [...]
Potassium is the most abundant monovalent cation in plant tissue. It is highly mobile which explains why deficiency symptoms can occur so rapidly. The concentration of potassium is directly related to the physiological activity of the plant. That is why young plants have higher potassium levels than older mature plants. Potassium is essential in regulating [...]
Phosphorus (P) was first discovered by Hennig Brandt in Germany in 1669. It is ironic that the discovery was made when he was busy with an experiment with urine, sand and coal. Phosphorus is absorbed by the plant from the nutrient solution in the form of H2PO4-1 or HPO4-2 at pH values between 4.5 and [...]
Nitrogen is consumed in large amounts by the plant. Nitrogen is used in components such as amino acids all proteins enzymes co enzymes nucleic acids and chlorophyll. Dry weight analysis of plant material shows that on average nitrogen makes up about 6% of the dry weight. Nitrogen is taken up in two forms; nitrates (NO3-) [...]
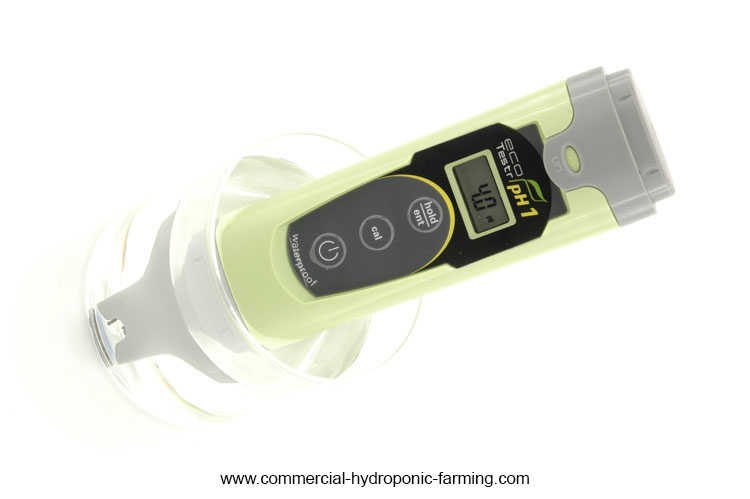
Adjusting ph of the water supply is crucial for maximum nutrient availability. It is seldom that the water supply, even from a well, is perfectly suitable (pH 5.8-6.8). The pH always needs some adjustment, either up or down. How to decrease the pH of a nutrient solution Lowering the pH is the most [...]
What is pH pH is the measurement of acidity or alkalinity of a solution. It is based on a logarithmic scale and starts at 0 and ends at 14 where the value 7 indicates a neutral, neither acid or alkaline. If a solution has a pH value below 7 it is called an acid. If [...]